The Windows version of the Python interpreter can be run from the command line the same way it’s run in other operating systems, by typing python or python3 at the prompt. But there’s a feature unique to the Python edition of Windows that makes it easier to manage multiple installed versions of the Python interpreter—the py launcher.
The py launcher—or just py for short—is a shortcut to all the installed versions of Python on your system. With a command-line switch, you can see at a glance all the Python interpreters you’ve installed and then invoke a specific version, whether it's 32-bit or 64-bit.
Install the py launcher
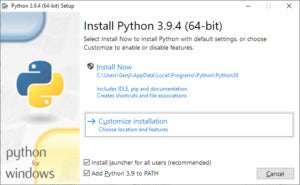
The py launcher is optionally installed during the setup process when you first install Python on Windows. At one point, you’ll be prompted to do so, as per the screenshots shown below.
The py launcher is installed directly into the Windows system directory, so it's always available. There is no downside to having py installed. You can always run the Python interpreter directly instead, and py doesn’t interfere with other behaviors.
 IDG
IDG
When installing Python on Windows, select the 'Customize installation' option during setup.
 IDG
IDG
In the next screen, make sure you've checked the 'py launcher' option.
When you type py at the command line, the launcher invokes the current default Python interpreter. py by itself will drop you into the Python REPL, which you can exit as you normally would by typing quit() or hitting Ctrl-Z.
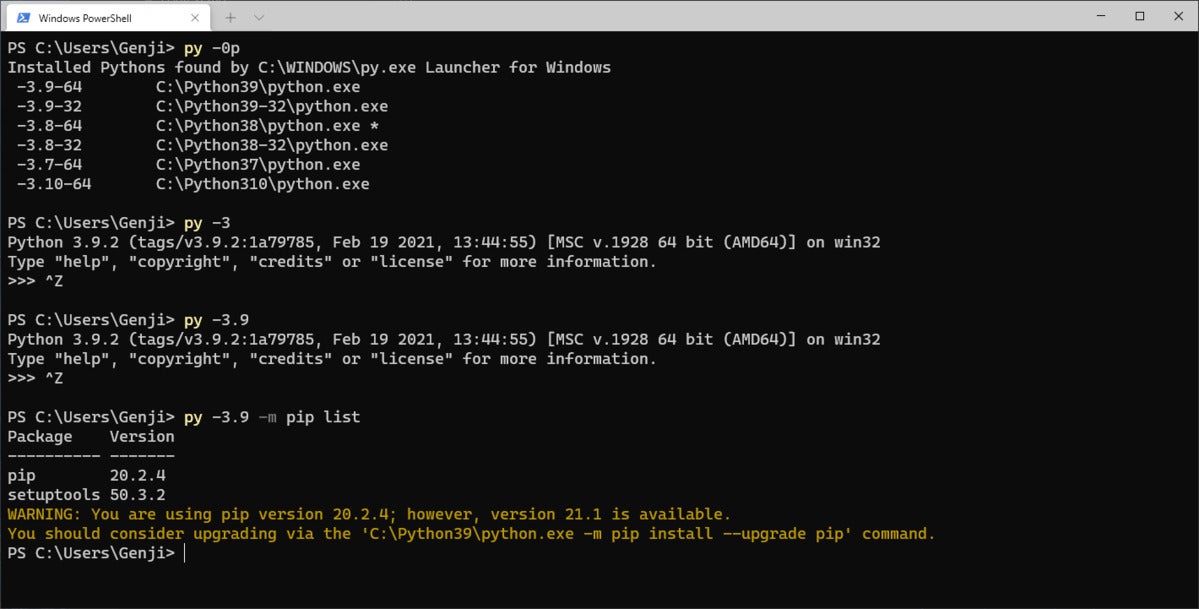
To see which versions of Python are available to py, type py -0p. You’ll be presented with a list of all the known interpreters in the system, their version numbers, and their full paths. The interpreter marked with an asterisk is the default.
To invoke a specific edition of Python, type py followed by the switch in the left-hand column for the appropriate version. For instance, to launch the 64-bit edition of Python 3.9, you would type py -3.9-64.
Note that if you provide only a version number, and not a bitness indicator, you’ll default to whichever version of Python is native to your machine’s processor type. On a 64-bit machine, that would be the 64-bit edition. So if you just typed py -3.9, you’d get the 64-bit version of Python 3.9.
 IDG
IDG
Four examples of the py launcher in action.
If you don’t specify a bitness, and only one bitness of a particular version is installed, that bitness will be loaded by default. In the above example, only the 64-bit version is installed, so if you type py -3.10, you'll get the 64-bit version of Python 3.10.
If you use just -2 or -3 as the version switch, Python will launch the most recent version of Python 2.x or Python 3.x, as indicated.
Upgrade py with new versions of Python
An important thing to keep in mind about the py launcher and upgrading Python versions: whenever a new version of Python is installed, the py launcher will be updated, as long as the Python version being installed is newer than the py launcher.
For instance, if you installed Python 3.8 and then Python 3.9, then 3.9 would upgrade py. But if you upgraded your Python 3.8 installation afterward, py wouldn’t be touched since the installer would detect that a newer version already existed.
This behavior can lead to some problems if you install a pre-release version of Python. As a general rule, when installing pre-release versions of Python in a system that has older production versions and an existing py launcher, don't install the py launcher for the pre-release version. Use the existing py.
If you install a pre-release Python with py, then later attempt to upgrade one of the release versions along with the py launcher, the installer will see a "newer" version of the py launcher (the one installed with the pre-release version) and abort the install process for the older-version upgrade.
Run Python scripts with py
To run a Python script with the py launcher, simply substitute py and its command-line switches for python or python3. For instance, here is the command typically used to upgrade pip by running it as a module:
python -m pip install -U pip
If we have the py launcher, we just type:
py -m pip install -U pip
To select a specific installation of Python, just pass the version as the first element in the argument list. Any arguments provided after the version are passed along as per usual.
py -3.9 -m pip install -U pip
Set the default Python for py
If you want to ensure that a given Python instance runs by default when you run py, you can do so in a few different ways. The methods are evaluated in this order:
- The active virtual environment. If you’re running
pyfrom a shell session where a Python virtual environment is active, the virtual environment’s edition of Python will be associated withpyby default. You can always override this by providing a specific version switch. - The shebang line in the script. Python scripts that begin with a line in the format of
#!/path/to/python python3or#!"C:\Python3.3\python.exe"will be run with the interpreter specified there. - The
PY_PYTHON2orPY_PYTHON3environment variables, when using the-2or-3switch. - The
PY_PYTHONenvironment variable. If you set a version number (e.g.,3.9-64or just3.9) with eitherPY_PYTHONor the previously mentioned environment variables,pywill default to launching that version.






